Blood is fluid connective tissue that circulates throughout the body. Why is it considered to be fluid connective tissue instead of just a fluid? It is composed of living cells suspended in plasma, the liquid that makes up around 55% of the blood. Plasma transports blood cells, proteins, electrolytes, hormones, and nutrients throughout the body. It also brings waste products from the body tissues to the urinary system, where the kidneys filter them out of the blood.
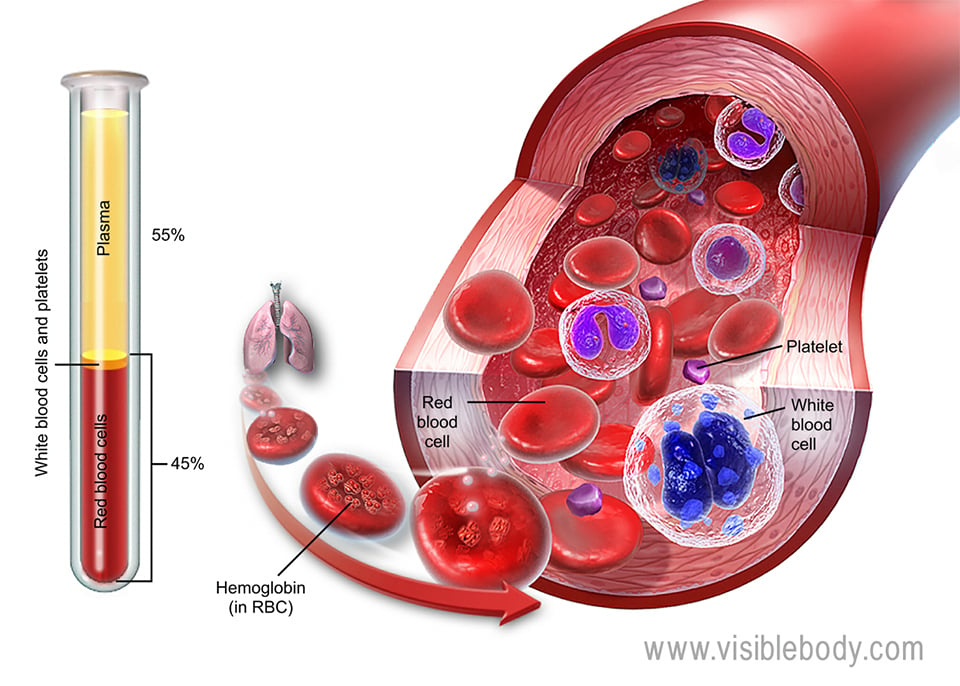
There are three broad categories of blood cells that have important functions. Red blood cells, or erythrocytes, carry oxygen from the lungs out to the rest of the body. White blood cells, or leukocytes, help protect the body from pathogens. There are five different types of leukocytes that combat infection in different ways. Platelets, or thrombocytes, clump together and form clots to repair torn blood vessels.
Blood has five principal functions that make it essential for a person’s survival:
Red bone marrow contains hematopoietic stem cells, or hemocytoblasts, which divide and differentiate into myeloid and lymphoid stem cells.
Myeloid stem cells give rise to red blood cells, platelets, and myeloblasts—cells that differentiate into myeloid white blood cells: neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, and monocytes.
Lymphoid stem cells give rise to lymphoblasts, which differentiate into white blood cells classified as lymphocytes: B cells, T cells, and natural killer (NK) cells.
Myeloid white blood cells are the mature, differentiated forms of myeloblasts in the red bone marrow. There are two varieties of myeloid white blood cells: granular and agranular.
Granular myeloid white blood cells include neutrophils (the most numerous type of white blood cell), basophils, and eosinophils. These types of white blood cells have granules in their cytoplasm and nuclei with multiple lobes.
In contrast, monocytes are agranular myeloid white blood cells. They do not have cytoplasmic granules, and their nuclei are not lobed.
Lymphoid white blood cells are the mature, differentiated forms of lymphoblasts, which are descended from lymphoid stem cells in the red bone marrow. Lymphoid white blood cells are called lymphocytes, a category which includes B cells, T cells, and natural killer cells. Like monocytes, B and T lymphocytes are agranular, and their nuclei are not lobed. NK cells are granular—in fact, they are often referred to as large granular lymphocytes.
An article from the Leukaemia Foundation describing blood formation.
Definition of hematopoietic stem cell from the National Cancer Institute.
Lecture notes about blood and body defenses from Eastern Kentucky University.
“What is plasma?” from the University of Rochester Medical Center Health Encyclopedia.
When you select "Subscribe" you will start receiving our email newsletter. Use the links at the bottom of any email to manage the type of emails you receive or to unsubscribe. See our privacy policy for additional details.