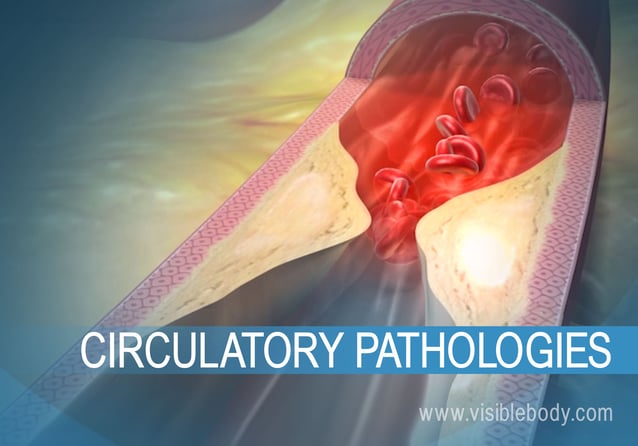
The circulatory system, also called the cardiovascular system, includes the heart and the network of blood vessels that circulate blood throughout the body. Several diseases and disorders can affect this system. Below are some of the most common pathologies.
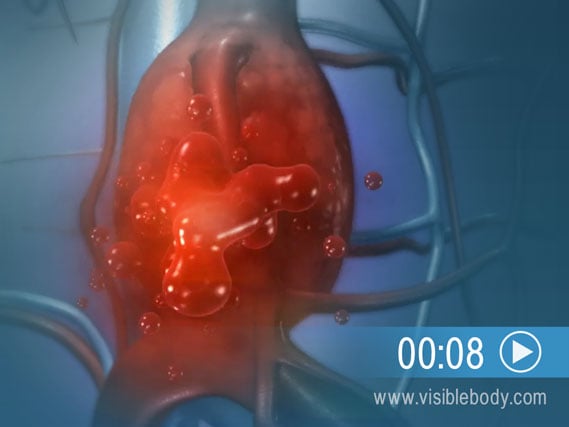
Oxygenated blood pumped from the left ventricle of the heart enters the aorta. The aorta is the largest artery. It branches into the systemic arteries that supply most regions of the body. In an abdominal aortic aneurysm, the wall of the aorta weakens in the area of the abdomen, which is usually due to high blood pressure. A bulge develops. The wall weakens further and then ruptures, causing internal bleeding. Voice over: In an abdominal aortic aneurysm, the wall of the aorta weakens and a bulge develops. Then it ruptures, causing internal bleeding.
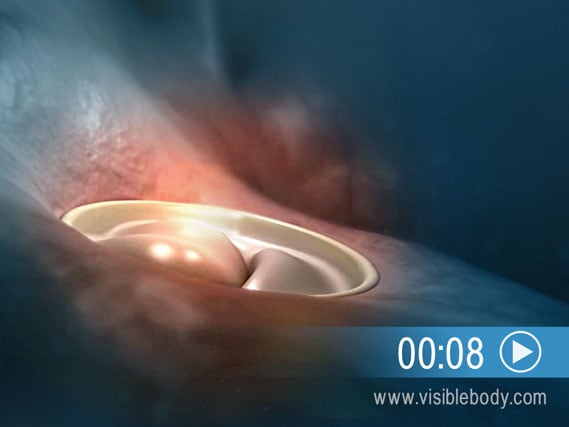

The mitral valve is one of the four heart valves. It controls proper blood flow from the left atrium into the left ventricle. In mitral valve prolapse, the valve bulges inward and does not close properly. Most people with mitral valve prolapse are born with it. In rare cases, blood may leak back into the atrium, a condition called mitral valve regurgitation.
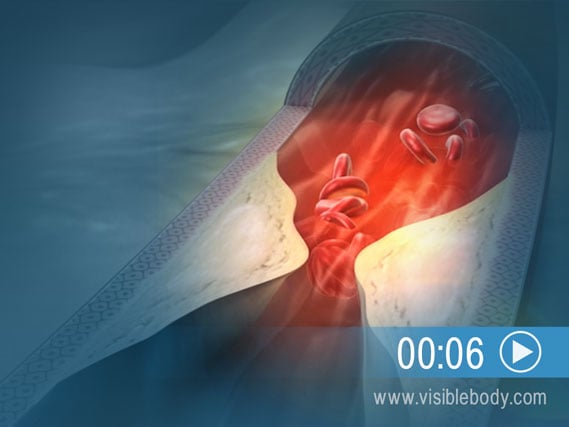

Coronary artery disease (CAD) develops as cholesterol and plaque accumulate on the interior walls of coronary arteries. This buildup is called atherosclerosis. The arteries become increasingly blocked, compromising the flow of oxygen-rich blood to heart tissue. If left untreated, the blockage can lead to chest pain and to a heart attack.
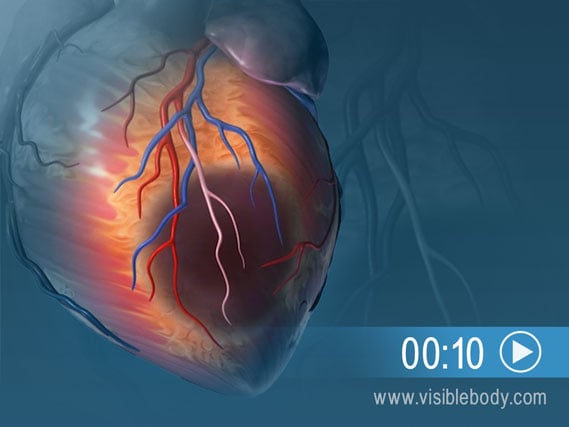
A myocardial infarction, or heart attack, happens when blood flow to heart tissue is obstructed. This can occur from a buildup of plaque in the walls of coronary arteries (as in coronary artery disease). Because oxygenated blood cannot reach part of the heart muscle that muscle dies or is damaged. The heart weakens and suffers a severe decrease in pumping ability. Signs of a heart attack include chest discomfort (pressure, squeezing, or pain), shortness of breath, nausea, and lightheadedness.
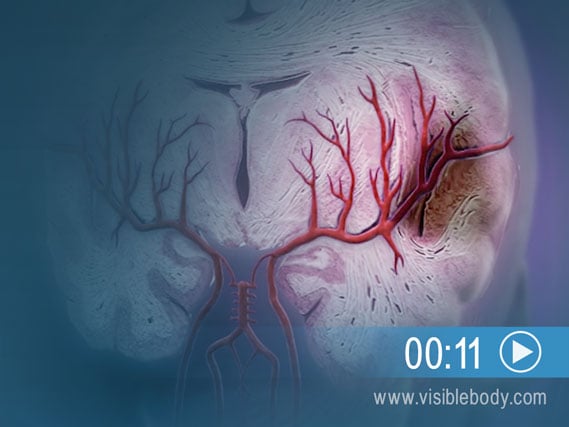
If a blood clot forms in the carotid artery in the neck, some of it will break off and travel into the arteries supplying the brain. The clot may then lodge in one of those arteries, cutting off blood supply to part of the organ. This pathology is called an ischemic stroke. The lack of blood supply destroys brain tissue and causes neurological damage. Another type of stroke, called a hemorrhagic stroke, occurs when an artery in the brain bursts and blood flows into the brain.
Understanding how cells become coronary vessels may lead to advances in repairing heart damage from Science Daily News.
A list of common medical tests for diagnosing heart conditions, from HealthyWA (a publication of the Department of Health of the Government of Western Australia).
Visible Body Web Suite contains animations detailing normal physiology and common pathologies.
When you select "Subscribe" you will start receiving our email newsletter. Use the links at the bottom of any email to manage the type of emails you receive or to unsubscribe. See our privacy policy for additional details.