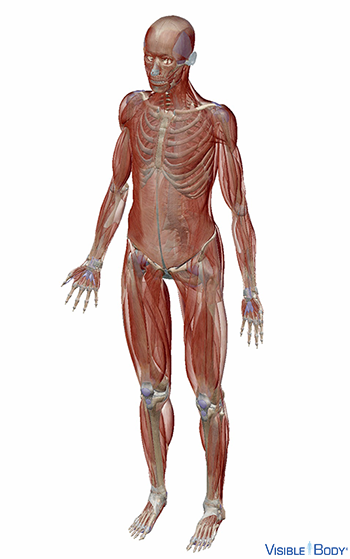
The muscles that move the human skeleton vary greatly in shape and size and extend to every part of our bodies. The muscular system contains over 600 skeletal muscles alone, which make up about 40% of our mass. See it in 3D!
System: Muscular, Skeletal
Region: All
At the simplest level, muscles allow us to move. They take direct instruction from the specific nerves that innervate each muscle. See it in 3D!
System: Muscular
Region: All
Pathologies: Muscular dystrophy, myositis, tendinitis
Skeletal muscles are attached to the skeleton by tendons.
System: Muscular, Skeletal
Region: All
Pathologies: Muscular dystrophy, myositis, tendinitis
Cardiac muscle, found only in the myocardium of the heart, contracts in response to signals from the cardiac conduction system to make the heart beat.
System: Muscular
Region: Heart
Skeletal muscles attach to the bones of the skeleton and contract voluntarily to produce movement. Skeletal muscle tissue is composed of long cells called muscle fibers that have a striated appearance.
System: Muscular
Region: All
Smooth muscle lines the gastrointestinal tract, blood vessels of the circulatory system, urinary tract, and reproductive organs.
System: Muscular
Region: All
Skeletal muscles are attached to the skeleton by tendons. The areas where the tendons attach the muscles to two articulating bones are called the origin and insertion points.
System: Muscular
Region: All
A muscle that contracts to generate the main force of an action is called the prime mover, or the agonist, for that action. Muscles that perform the paired and opposing action are called the antagonists.
System: Muscular
Region: All
Flexion: decreasing the angle between two bones (bending).
Extension: increasing the angle between two bones (straightening a bend).
System: Muscular
Region: All
Abduction: moving away from the body’s midline.
Adduction: moving toward the body’s midline.
System: Muscular
Region: All
Pronation: rotating the forearm so the palm is facing backward or down.
Supination: rotating the forearm so the palm is facing forward or up.
System: Muscular
Region: All
Elevation: moving a body part up.
Depression: moving a body part down.
System: Muscular
Region: All
Protraction: moving a bone forward without changing the angle.
Retraction: moving a bone backward without changing the angle.
System: Muscular
Region: All
Inversion: turning the sole of the foot inward.
Eversion: turning the sole of the foot outward.
System: Muscular
Region: All
Dorsiflexion: bringing your foot upward toward your shin.
Plantarflexion: depressing your foot.
System: Muscular
Region: All
Synergists are muscles that assist the prime mover in its role. Stabilizers act to keep bones immobile when needed.
System: Muscular
Region: All
Function: Your back muscles, for example, are stabilizers when they are keeping your posture sturdy.
Muscle contraction begins when the nervous system generates a signal. The signal, an impulse called an action potential, travels through a type of nerve cell called a motor neuron. The neuromuscular junction is the name of the place where the motor neuron reaches a muscle cell.
System: Muscular
Region: All
Acetylcholine is a widespread neurotransmitter found in the CNS and at neuromuscular junctions between peripheral nerves and muscles.
System: Muscular
Region: All
M. sternocleidomastoideus
The sternocleidomastoid muscle (r, l) is a muscle in the neck that is also often classified with the lateral cervical muscles.
System: Muscular
Region: Neck
Function: Draws head toward shoulder of same side, rotates head to opposite side, flexes cervical part of vertebral column, assists in elevating the thorax
Pathologies: Muscular dystrophy, myositis
The rotator cuff (r, l), a subdivision of the posterior shoulder girdle, comprises a group of muscles responsible for stabilizing the glenohumeral joint. These muscles also contribute to the proper motion of the upper limbs. See it in 3D!
System: Muscular
Region: Shoulder
Pathologies: Muscular Dystrophy, myositis, rotator cuff tendinosis
M. deltoideus (pars clavicularis, pars acromialis, pars spinalis)
The deltoid (r, l), one of the posterior shoulder joint muscles that form the muscular system’s shoulder girdle, is a large, thick, triangular muscle that covers the shoulder joint in front, behind, and laterally.
System: Muscular
Region: Shoulder
Function: It allows flexion and medial rotation of the humerus.
Pathologies: Muscle cramps, muscular dystrophy, myositis, polio/post-polio syndrome, sprains, strains, tendinitis
M. pectoralis major
The pectoralis major (r, l), one of the anterior shoulder muscles that form the muscular system’s shoulder girdle, is a thick, fan-shaped muscle situated at the upper and forepart of the chest.
System: Muscular
Region: Thorax
Function: Adducts and flexes the arm and rotates it medially (inward)
Pathologies: Muscular Dystrophy, myositis
M. latissimus dorsi
The latissimus dorsi (r, l) is one of the posterior shoulder joint muscles that form the muscular system’s shoulder girdle. The latissimus dorsi is a triangular, flat muscle that covers the lumbar region and the lower half of the thoracic region and is gradually contracted into a narrow fasciculus at its insertion into the humerus.
System: Muscular
Region: Thoracic/shoulder region
Function: The functions of the latissimus dorsi include joining the upper limb with the axial skeleton and facilitating the proper motion of the upper limb.
Pathologies: Muscular Dystrophy
M. trapezius
The trapezius (r, l), a muscle of the posterior thorax that acts on the pectoral girdle, is a flat, triangular muscle covering the upper and back part of the neck and shoulders.
System: Muscular
Region: Neck, Shoulder, Thorax
Function: Rotation, retraction, elevation, and depression of scapula, levitate clavicle; extends the neck; stabilizes the shoulder
Pathologies: Muscular dystrophy, myositis
M. biceps brachii (caput longum, caput breve)
Biceps brachii, long head (r, l) and biceps brachii, short head (r, l) are both anterior flexor muscles of the elbow joint. See it in 3D!
System: Muscular
Region: Upper Limb (Arm)
Function: Flexes and supinates the elbow
Pathologies: Muscular dystrophy, myositis, sprains and strains, tendinitis.
M. triceps brachii (caput mediale, caput longum, caput laterale)
The triceps brachii, a large upper limb muscle named for its three heads, comprises the triceps brachii tendon (r, l) and three heads: lateral (r, l), long (r, l), and medial (r, l).
System: Muscular
Region: Upper Limb (Arm)
Function: Extends the forearm at the elbow
Pathologies: Muscular dystrophy, myositis, tendinitis
M. rectus abdominis
The rectus abdominis (r, l) is a long, flat muscle of the abdomen. The rectus abdominis extends along the whole length of the front of the abdomen and is separated from its fellow of the opposite side by the linea alba. See it in 3D!
System: Muscular
Region: Abdomen
Function: Flexes vertebral column, tenses abdominal wall, compresses abdominal viscera
Pathologies: Muscle cramps, muscular dystrophy, myositis
M. obliquus externus abdominis
The external oblique (r, l), a muscle of the abdomen situated on the lateral and anterior parts of the abdomen, is the largest and the most superficial of the three flat muscles in the abdomen.
System: Muscular
Region: Abdomen
Function: Bilaterally: compresses abdomen and flexes (bends) the spine. Unilaterally: laterally flexes trunk to same side and rotates trunk to the opposite side.
Pathologies: Muscle cramps, muscular dystrophy, myositis.
M. piriformis
The piriformis muscle (r, l) is one of the lateral rotators of the hip that also facilitates hip abduction and extension.
System: Muscular
Region: Hip
Function: External rotation, abduction, and extension of the hip joint; aids in stabilization of the hip
Pathologies: Muscular Dystrophy
The muscles of the gluteal region are muscles located in the hip and gluteal region of the lower limbs and originate from the pelvis, insert into the femur, and act on the hip joint. The gluteal muscles include the gluteus minimus (r, l), the gluteus medius (r, l), and the gluteus maximus (r, l). See it in 3D!
System: Muscular
Region: Hip
Pathologies: Muscular dystrophy, myositis
The muscles of the proximal leg (r, l), a region within the muscular system’s lower limbs, are a group of muscles in the region between the hip joint and the knee joint—an area commonly called the thigh. The muscles of the thigh are further divided into anterior (r, l), medial (r, l), and posterior (r, l) compartments. See it in 3D!
System: Muscular
Region: Lower limbs
Pathologies: Muscular dystrophy, myositis
The quadriceps include the rectus femoris (r, l), and the vastus medialis (r, l), the vastus intermedius (r, l), and the vastus lateralis (r, l). See it in 3D!
System: Muscular
Region: Lower Limb
Function: All are extensors of the knee innervated by the femoral nerve (L02-L04).
Pathologies: Muscular dystrophy, myositis
The muscles of the posterior compartment are the biceps femoris, long head (r, l), the biceps femoris, short head (r, l), the semimembranosus (r, l), and the semitendinosus (r, l). See it in 3D!
System: Muscular
Region: Lower Limb
Pathologies: Muscular dystrophy, myositis
The muscles of the distal or lower leg are a group of muscles located between the knee joint and the ankle joint that act on the ankle joint, facilitating movement of the foot and toes. The muscles of the posterior compartment include the flexor digitorum longus (r, l), the flexor hallucis longus (r, l), the tibialis posterior (r, l), the popliteus (r, l), the plantaris (r, l), and the muscles of the triceps surae, the gastrocnemius (r, l) and the soleus (r, l). See it in 3D!
System: Muscular
Region: Lower Limb
Pathologies: Muscular dystrophy, myositis
M. gastrocnemius
The gastrocnemius (r, l) is a superficial two-headed muscle of the posterior compartment of the leg and one of the two muscles that make up the triceps surae.
System: Muscular
Region: Lower limbs
Function: Plantarflexion of foot, flexes leg at knee joint
Pathologies: Muscle cramps, muscular dystrophy, myositis, Polio and Post-Polio Syndrome
M. soleus
The soleus (r, l) is a superficial muscle of the posterior compartment of the leg and one of the two muscles that make up the triceps surae.
System: Muscular
Region: Lower Limb
Function: Plantarflexion of foot
Pathologies: Muscular dystrophy, myositis
Tendo calcaneus
The gastrocnemius (r, l) and soleus (r, l) of the posterior compartment (r, l) of the leg (r, l) unite their tendons to make the achilles tendon.
System: Muscular
Region: Lower Limb
Function: The tendon inserts on the calcaneus.
Pathologies: Muscular dystrophy, myositis, tendinitis
When you select "Subscribe" you will start receiving our email newsletter. Use the links at the bottom of any email to manage the type of emails you receive or to unsubscribe. See our privacy policy for additional details.