Diseases and disorders of the digestive system can involve infection or damage to organs and other tissues and structures. They may also affect actions of the digestive system, such as the sealing of the esophagus from stomach acids or the free flow of fluids through the bile ducts. Symptoms can arise during digestion or may be chronic.
Read on to learn about five of the most common diseases and disorders.
Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix, a narrow tube attached to the base of the cecum. Once thought to have no function, the appendix is now known to function as part of the lymphatic system. A blockage inside of the appendix can cause appendicitis. The main symptom is pain on the lower right side of the abdomen that gets worse over time. If not treated, the appendix can burst and spread infection into the abdomen.
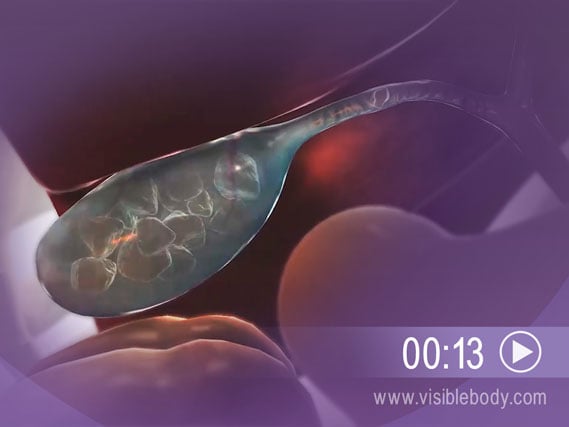
Gallstones are pieces of solid material that can form from stored bile in the gall bladder. They range from tiny specks to the size of golf balls. During digestion, gallstones can block the flow of fluid through the bile ducts. Signs of a gallstone attack include nausea, vomiting, or pain in the abdomen, back, or just under the right arm.
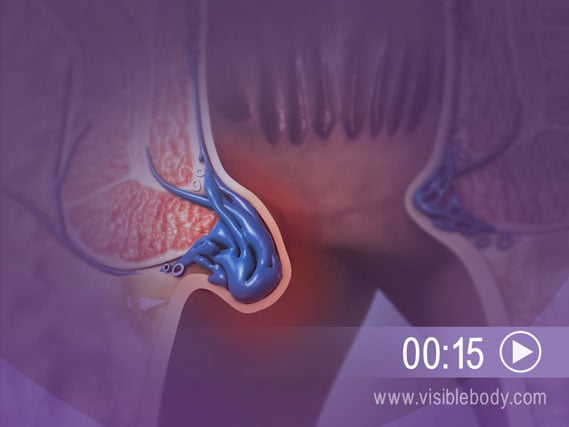
Hemorrhoids are swollen, inflamed veins around the anus or lower rectum. Straining for bowel movements can cause hemorrhoids. Pregnancy, diarrhea, and chronic constipation are contributing factors. They can develop under the skin around the anus (as external hemorrhoids) or inside the anus (as internal hemorrhoids). Further straining or irritation when passing stool can damage a hemorrhoid's surface and cause it to bleed.
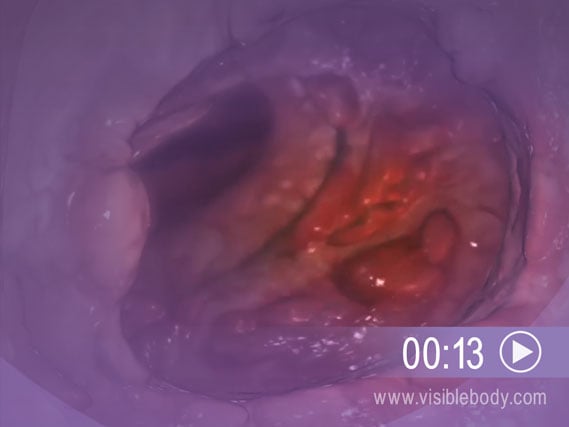
Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease that affects the large intestine. It causes inflammation and sores (ulcers) in the innermost lining of the colon and rectum. This leads most often to abdominal pain or to diarrhea with blood and pus. Ulcerative colitis is a chronic condition characterized by alternating periods of flare-up and remission, when the symptoms of the disease disappear.
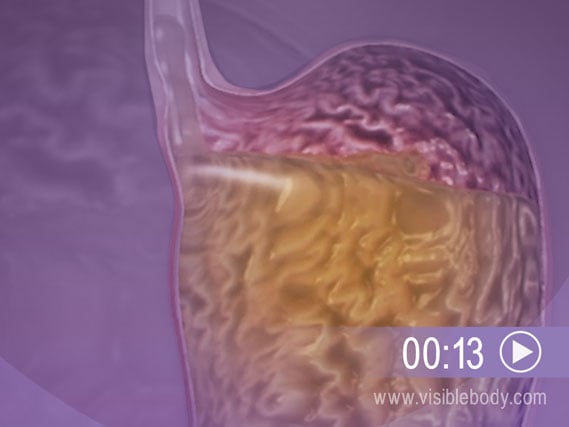
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a chronic disease of the digestive system. GERD usually occurs when the lower esophageal sphincter, a muscle at the end of the esophagus, does not close properly. This allows stomach acid to leak back, or reflux, into the esophagus and irritate it. Symptoms include heartburn, regurgitation, and the taste of stomach fluid in the back of the mouth.
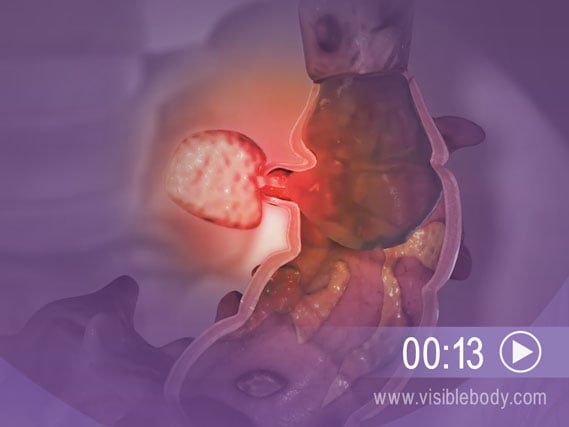
Diverticulosis occurs when small pouches form in the wall of the large intestine. Most people with diverticulosis don't have symptoms. However, if feces get trapped in the pouches and bacteria grow, inflammation and infection result. This is called diverticulitis. Most often it causes abdominal pain. Other symptoms include fever, nausea, and constipation.
The MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia entry for digestive diseases.
A description of digestive system diseases from Des Moines University’s online medical terminology course.
Visible Body Web Suite provides in-depth coverage of each body system in a guided, visually stunning presentation.
When you select "Subscribe" you will start receiving our email newsletter. Use the links at the bottom of any email to manage the type of emails you receive or to unsubscribe. See our privacy policy for additional details.